 Although we are used to using names (e.g. www.google.com) when surfing the Internet, the Internet works on numbers called IP addresses.
Although we are used to using names (e.g. www.google.com) when surfing the Internet, the Internet works on numbers called IP addresses.
The process of translating a computer name or domain name to a IP address is known as name resolution and for services on the Internet this is done by a service called domain name System (DNS).
The DNS (Domain Name systems) is a system for providing name resolution for computers located on the Internet.
The name,known as a Domain Name., has a specific syntax and looks something like www.google.com.
DNS services are provided by Google and other providers like your ISP( Internet Service provider).
Computer Names and Domain names –
A computer name doesn’t have a structure and is common on windows home networks. e.g. workstation6
Domain names have a structure and look like this workstation6.mydomain.com.
Domain names aren’t common on home networks as home networks don’t usually have many devices, and don’t have a local DNS service.
Name Resolution
However on home networks it is common to use names when accessing services on other machines on a home network.
When viewing other machines in network neighborhood they are listed by name and not IP address.
Windows machines have several name resolution methods, and in resolving a name a windows machine might try several different methods.
The order in which it tries these methods depends on the name i.e. is it a domain name, and the service e.g.An Internet service like http, or a local service like net use etc
The methods used for traditional Windows services like file sharing are:
- Local Hosts file
- Netbios Name Cache
- Broadcast
Local Hosts File
On windows XP,windows 7 the hosts file is located in c:\windows\system32\drivers\etc\,
Note: It may be hidden so will need to enable view hidden files to see it and you may need to open it as an administrator.
Here is the basic host file example:

Netbios Name Cache
When a windows machine resolves a name it stores it temporarily in memory.
This means that if you access that machine again it doesn’t have to resolve the name again.
You can view this cache using the nbtstat command.
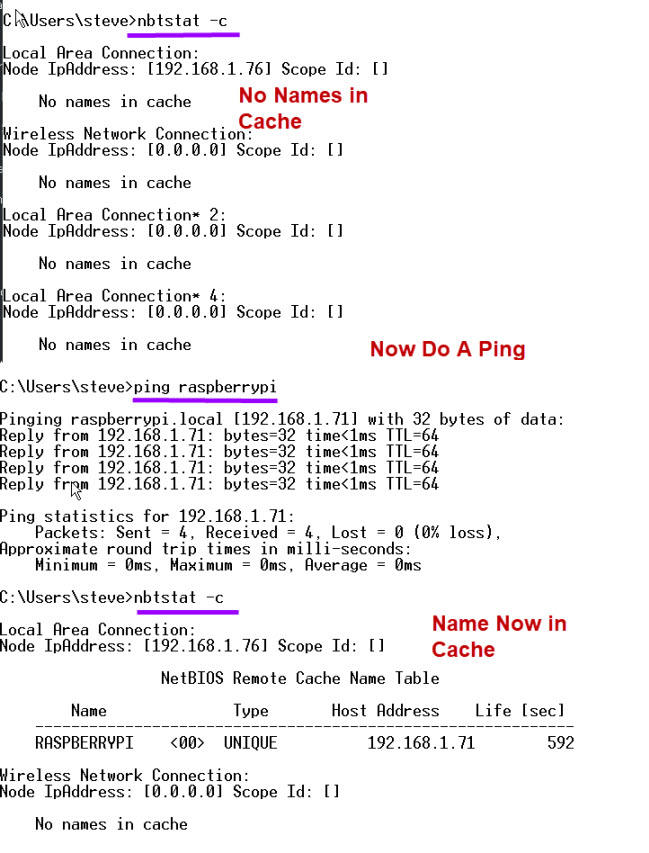
Broadcast
This is the main name resolution method on a windows home network.
A machine simple ask all other machines if they have a particular name and if they do then they respond with their IP address.
Broadcasts don’t work across routers but this isn’t normally a problem on home networks as they only have one router which is facing the internet and so doesn’t affect name resolution on the home network
Other Methods
in other tutorials you might find LMhosts file and Wins mentioned.
LMhosts is basically a hosts file but for windows names. It requires configuring and is not normally used. It is located inthe same folder as the hosts file.
Wins in the windows equivalent to DNS and requires a server running the service and again not normally used
MultiCast DNS – Multicast DNS is a new addition to name resolution which has recently been added to all operating systems including Windows. This is likely to become the default mechanism in the future. See Understanding Multicast DNS and Service discovery. (coming soon)
Common Questions and Answers
Q- Can I install and configure my own local DNS server for local name resolution?
A- Yes but it is not a simple task. On linux (Pi) the popular choice is DNSMasq.
Q- What happens on mixed networks i.e. windows and Linux?
A- It depends on how they are configured. The screen shot below shows that I can ping a raspberry pi from my Windows machine.
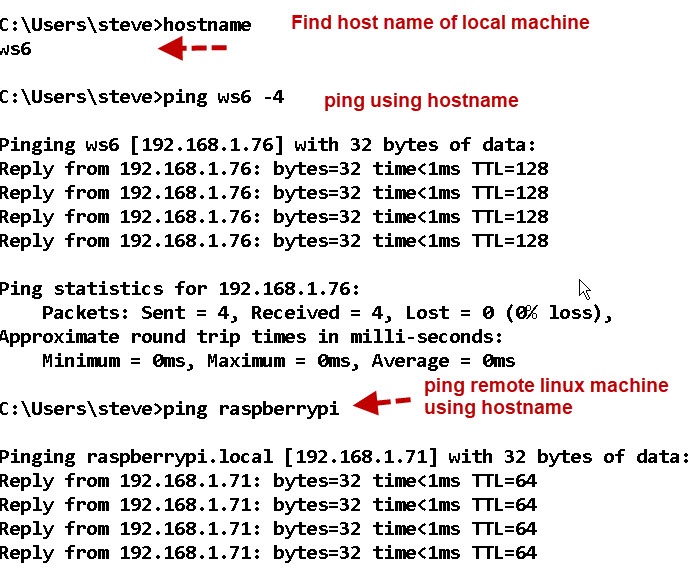
However it may not work from pi to windows. If not then you need to edit the /etc/nsswitch file
change:
hosts: files mdns4_minimal [NOTFOUND=return] dns
to
hosts: files mdns4_minimal [NOTFOUND=return] dns wins
and install libnss-winbind
using:
sudo apt-get install libnss-winbind
See end of this thread
Local Domain Name Home Network
The top level domain name .local has been reserved for home networks and is used by MDNS (multicast DNS).
If you are setting up your own local DNS server then the list of recommend names is: (Appendix G. Private DNS )
- intranet
- internal
- private
- corp
- home
- lan
For home networks .home is a good choice.
Q- What is the .local Domain name?
A- This reserved domain name is used by the mdns service.
Q- Do I need a DNS server on my home network?
A- It depends on how many computers/devices you have a what you do. If you have local services and or smart home devices then having a domain name in stead of just an IP address makes it much easier to manage. See Setting Up A DNS Server using DNSMasq.
Resources:
IBM- Learn Linux Netbios and Wins
Related Tutorials:
- Setting Up A Static IP Address on Windows 10
- Home Network Addressing
- Understanding DHCP on Home Networks
- What is Dynamic DNS? Why use it
- Multicast DNS (MDNS) on Home Networks
Year 2021 and this still does not work consistently across different OS’es and routers. This is crazy.
Thanks. By what protocol does a machine ask all other machines if they have a particular name?
MDNS (multicast DNS) https://stevessmarthomeguide.com/multicast-dns/
Thank for pointing me to dnsmasq. I was trying to find out how to centrally resolve a host name to ip address, in my lab.