The Zigbee network protocol is a common protocol used on home and industrial networks.
Although it is designed to be easy to set up it is important that you have a basic understanding of how it works.
These are my personal notes on Zigbee that be be helpful if you are new to the protocol.
What is Zigbee? – Zigbee is a low power, low data rate (250kbps) wireless protocol used primarily for Home automation and industrial control, building automation,sensor data collection etc – Wiki
Zigbee devices have a range (1 hop) of 10 to 20m and to be certified must have a battery life of 2 years.
Zigbee Network Topologies
Zigbee networks can be configured to operate in one of three topologies.
- Star
- Tree
- Mesh
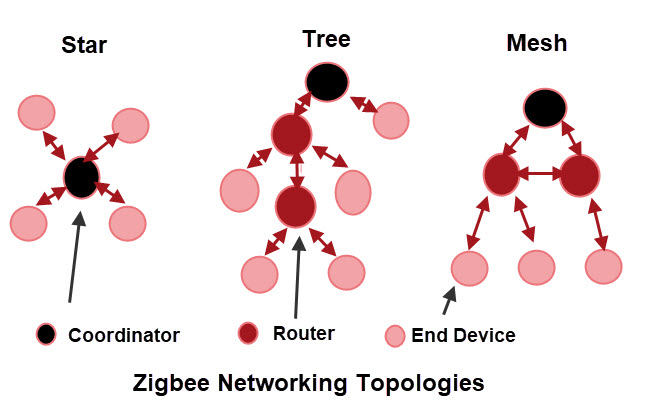
Devices can be split into:
- Full Function Device (FFD)
- Reduced Function Device (RFD
Full Function Device (FFD)- Can communicates with all node types and can operate in one of three modes:
- PAN Coordinator: Sends beacon frames, provides routing information, manages short, network-specific addresses. Every network requires one
- Router.-Relay messages between nodes. Not required in simple networks.
- Normal End device.-Sends and receives messages. The only node type that can sleep.
There must be 1 coordinator on a Zigbee network.
Reduced Function Device (RFD): Can only talk to a single
FFD. These are end nodes. Example a smart lock,switch ect
Zigbee Network Addresses
All devices have a 64bit MAC address assigned by the manufacturer.
The MAC address is mapped to a unique 16 bit network address by the coordinator and assigned when the device joins the network. This is the Short address.
The coordinator has a network address of 0.
Zigbee also provides support for group addresses which allows message delivery to multiple nodes.
Device Binding
Zigbee also supports device binding were you can bind a device e.g a switch to another device e.g a bulb or to a group of devices.
Message Types
Zigbee supports three messaging types as per IP networks.
- Unicast– one to one
- Multicast -1 to a group
- Broadcast -1 to all
Groups
Zigbee supports groups which let you assign devices to a group which is effectively a cluster of endpoints.
This allows you to address multiple devices with a single command.
PAN Address
This is a 16 bit address assigned by the coordinator when the network is created. It is equivalent to the IP network address.
The PAN address must be unique.
Application Addresses
A Zigbee node can support up to 240 applications.
Each application is assigned an endpoint number in the range 1-240. This is similar to tcp/ip ports.
A broadcast endpoint of 255 is also available.
Encryption
Data can be encrypted at one of three levels:
- MAC
- Network
- Application
Encryption uses AES-128 and shared keys.
Example Zigbee Devices
- Philips Hue lighting and other device like motion sensors
- Amazon Echo dot Plus (Zigbee hub)
- Bosch Security Systems
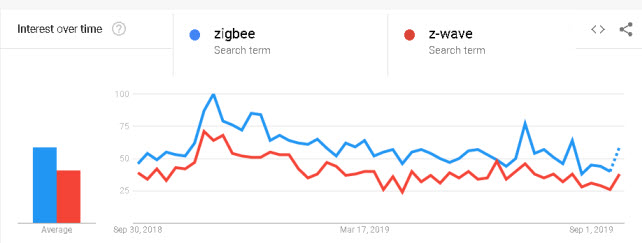
Popularity ZigBee vs Z-Wave
Video
Example Network
The following is a schematic of my test network that consists of a coordinator (zigbee2mqtt) a router and 3 end devices.
I placed the temperature sensor about 30 meters from the coordinator and the router in between the two.
Without the router the temperature sensor could not communicate with the coordinator.
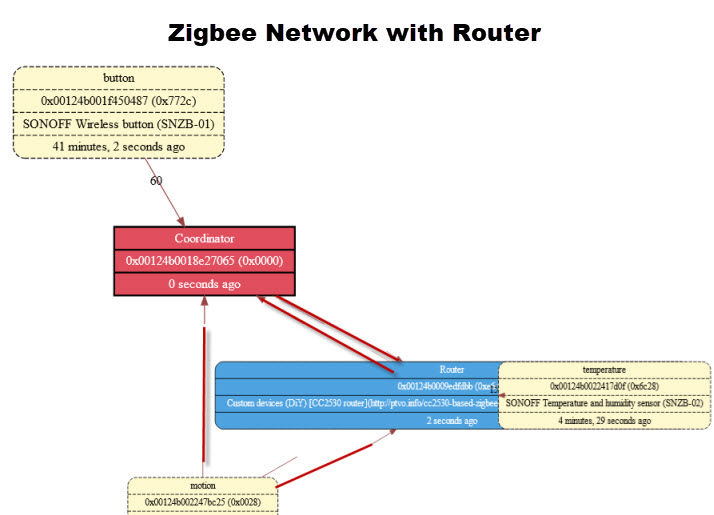
There was no manual configuration necessary the router found the coordinator and the temperature sensor found the router.
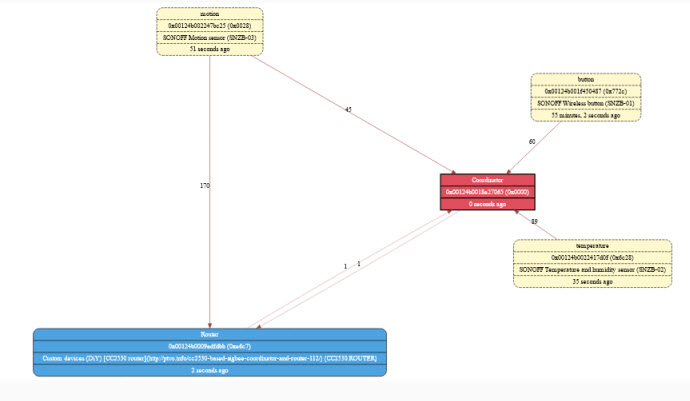
When I moved the temperature sensor back near to the coordinator the network reformed as shown below. (router in blue,coordinator in red)
Resources:
- An overview of Zigbee networks for testers
- Getting started with Zigbee pdf
- Zigbee overview slides
- ZigBee Overview
- Zigbee vs Zwave–
Related Tutorials
- Using Zigbee2MQTT
- Zwave Basics notes and resources
- Control Zigbee Devices Using Zigbee2MQTT with Home Assistant
- Build a Zigbee sniffer
- Beginners Guide to the Matter Protocol -Part 1
- Smart Homes and MQTT