 There are many different ways network nodes can be connected together.
There are many different ways network nodes can be connected together.
Common connection technologies used on home networks like Ethernet, Wi-Fi, Bluetooth etc are designed to work using a particular network topology.
Having an understanding of these topologies is important when structuring your home network.
Common home network topologies are:
- Bus
- Ring
- Mesh
- Star
- Hybrid
Each of these topologies has advantages and disadvantages this Network topologies article has a really good overview of each topology along with advantages and disadvantages.
Bus and Star Bus topology
Early Ethernet networks used a bus structure as Ethernet was originally designed to use a shred coaxial cable.
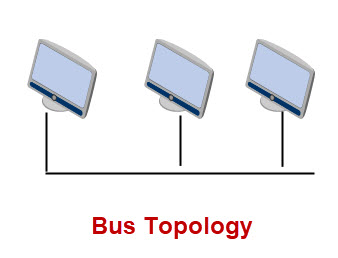
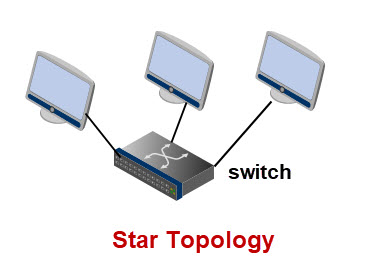
Modern Ethernet networks use UTP (unshielded Twisted pair) and switches creating a star bus (hybrid) structure, as do Wi-Fi Networks.
The diagram shows a typical home network structure which forms a star bus hybrid.
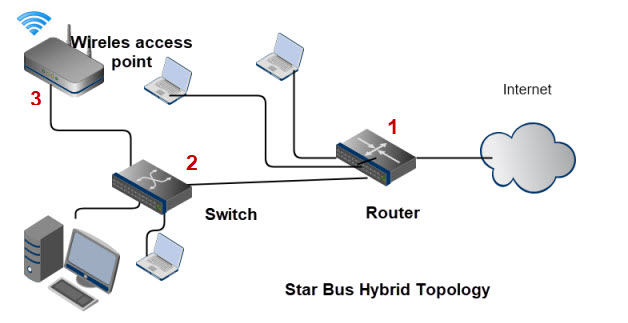
Points of Failure
Referring to the diagram above there are 3 main points of failure.
- Router or Internet connection affects all traffic
- Switch failure affects all connected devices
- Access point failure affects all Wi-Fi devices.
When designing your network it is always a good idea to try minimize these failure points.
On large corporate networks they build in redundancy using additional networking components, but on home networks this is usually not a viable option.
You might find this video interesting –How not to design a network ,but you should remember he is talking about corporate networks.
Mesh Networks
These can either be partial or fully meshed as shown in the diagram below:
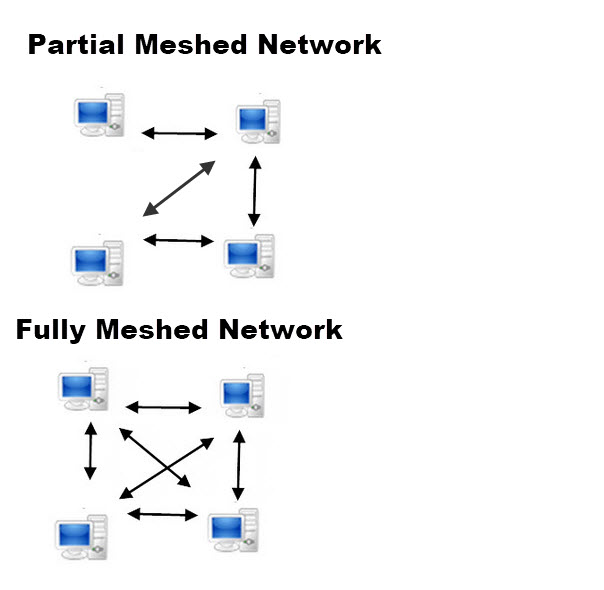
Meshed networks are highly resilient to failure but aren’t practical with a large number of nodes as too many connections are involved.
Ring Networks
Token ring is an example of a ring network but token ring is not used any more in modern network and so this type of network is seldom encountered
Network Topology- Physical vs Logical
How the nodes on a network communicate with each other can be very different to how they are physically interconnected.
Most Home and small office networks use a physical bus topology.
Common logical typologies are Peer to Peer and Client Server.
Client Server
The web (WWW) is a client server network at the logical level.
In a client server model a central server hosts information that the client want.
In the case of the web the server hosts web pages.
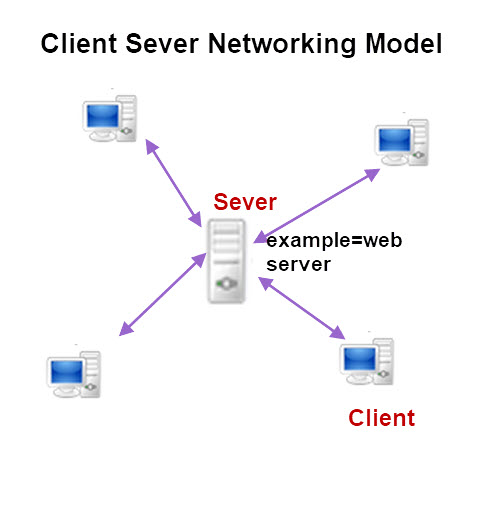
Advantages and Dis-Advantages
Client Server |
|
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Easy to backup | more difficult to set up |
| Better security | Requires a network administrator |
| Easy to Locate resources | Requires more powerful and expensive hardware |
| Single point of failure | |
Peer to Peer
Most home networks use peer to peer networking model.
Microsoft windows (all versions) supports this model.
In a peer to peer networking model a computer functions as both a client (workstation) and a server.
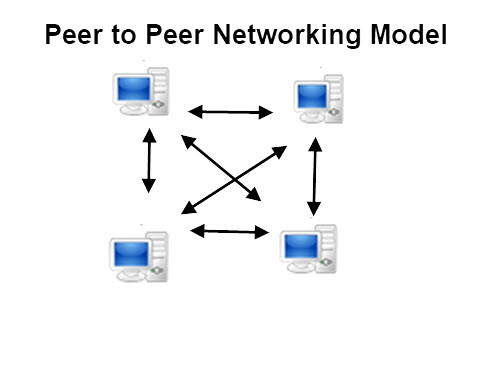
Advantages and Dis-Advantages
Peer To Peer |
|
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Easy to set up | Difficult to secure |
| No central administrator | Difficult to locate a resource |
| No single point of failure | Difficult to ensure data is backed up |
| No need for expensive server hardware | |
Smart Home Devices
Smart Home devices tend to use the client server model when using http for control. Each device will connect to a central (cloud based) server for configuration and control.
However if you use Tasmota devices the sensor itself acts as a server and is then controlled by an http client -See Using HTTP To Control Smart Home Devices.
Related tutorials and resources
- Basic Home Network Hardware Components, Devices and Services
- Basic Home Networking Course for Beginners
- Home Network troubleshooting