![]() The ping command is one of the most often used networking utilities for troubleshooting network problems.
The ping command is one of the most often used networking utilities for troubleshooting network problems.
You can use the ping command to test the availability of a networking device (usually a computer) on a network.
When you ping a device you send that device a short message, which it then sends back (the echo).
If you receive a reply then the device is working OK , if you don’t then:
- The device is faulty, disconnected, switched off, incorrectly configured
- Your network or the device you are working on is not working properly.
Note: In this tutorial we will use the ping command on Windows but it works the same on Linux
Ping Command Prompt
To use the ping command you go to the command line.
On Windows (XP,7) – Start Menu>Run and enter cmd to open a command prompt.
On Windows 10 type cmd into the search box and select the cmd prompt from the displayed programs.
You can use the ping cmd with an IP address or the computer/host name.
To ping an IP address go to a cmd prompt and enter:
Ping IP Address e.g. ping 192.169.0.1 or to ping a computer name:
ping computer name e.g. ping Computer1
The screen shot below shows how to use the command with an IP address.
I have shown both a failed ping (192.168.0.1), and a successful ping (192.168.1.1)
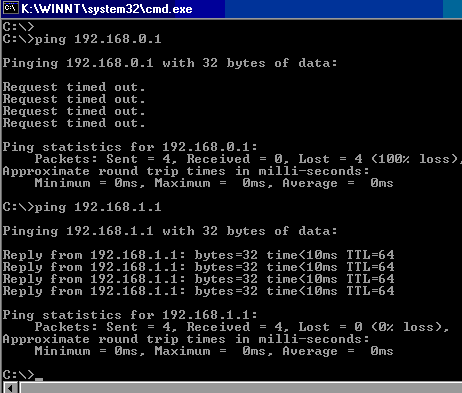
Note: a failed ping results in a request timed out response, and a success results in the reply from message with the round trip delay in milliseconds.
The screen shot below shows how to use the ping command with the computer name.
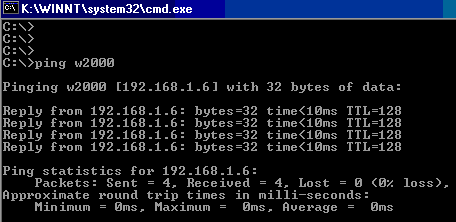
Although this is easier to use a computer name than the IP address, it is only good if it works..
If it fails it is not conclusive as there is an extra stage called name resolution involved, and that could be at fault.
Here is a quick video that takes you through the process.
Using Ping To Troubleshoot Home Network Problems
The most common use of the ping command is to troubleshoot and locate network connectivity problems.
The general idea is to ping each network interface between your machine and the destination machine.
When a ping fails it indicates a problem with that network segment.
To illustrate I have drawn a simple home network with a workstation and server separated by a router (home router/hub).
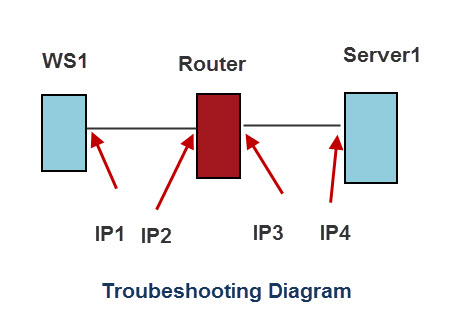
If the problem was that the workstation (WS1) cannot connect to the server, then the general procedure would be: On WS1
- Ping loop back address 127.0.0.1 — tests own protocol stack.
- Ping IP2
- Ping IP3
- Ping IP4
If all pings work except the IP4 ping then we know that there is a problem on the network between the router and server.
The Ping Command- Advanced Options
The ping command has various options (switches) which you can see by typing
ping /? at the command prompt
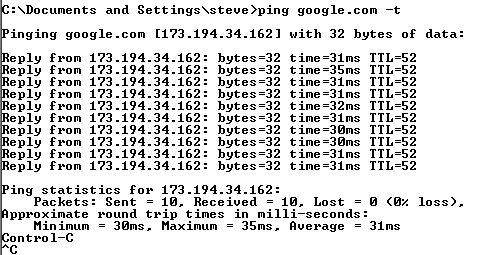
So for a continuous ping we type
ping IP address or name -t
e.g.
ping google.com -t
Here is the result
IPv6 Addresses
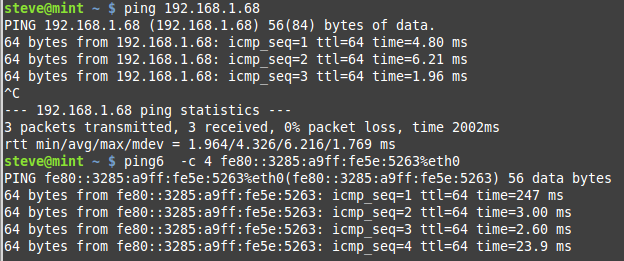
If you have IPv6 configured on your system then you can also ping ipv6 addresses
on Windows networks you need to use ping -6 at the cmd prompt
example — ping -6 hostname or IP address
and on Linux systems use ping6
example — ping6 -c 4 -I eth0 hostname or IP address
or
ping6 -c 4 IP address%eth0
Note: not using the Interface option may result in an Invalid Argument error
The screen shot below shows an IP4 and IP6 ping on linux
Common Questions and Answers
Q- What is the localhost?
A- On all operating systems localhost is the name given to your local machine and is resolved to the IP address 127.0.0.1.
Q- What is the Address 127.0.0.1?
A- This is known as the loopback address and is a special address assigned to your network interface.
Summary
The ping command is a networking utility available on all Operating systems that is used for troubleshooting on IP networks.
Related Articles and Resources
- Home network Addressing
- Home networking course
- Troubleshooting Home Network and Internet Connection Problems
what if the windows search bar is not working is there any other way to perform the PING?
You need a dos terminal. The windows +X gives a menu to select the run command
Thank you so much, i have really learnt from your website.