Network latency is the term used to describe network lag. It is the time taken for a packet to be sent and received over a network and decoded by the receiver.
It can be one way or two way depending on whether a response is required.
As an example if you tell Alexa to turn on the lights the latency or delay is the time taken for you issuing the command to the lights turning on.
Network Latency Causes
There are several factors that contribute to network latency they are:
- Distance
- Networking Media
- Networking Wireless technology
- Networking Protocol
- Network Congestion
- Intermediate Networking devices e.g switches,hubs, routers etc
- End devices and Services
Distance
This is the main cause of Latency and usually cannot be avoided. The lardger the distance the greater the delay.
Networking Media
On long distance networks you can have satellite links or cable links. Satellite links will have a higher latency than cable links.
Networking Wireless Technology
On home networks protocols like Zwave have a higher latency than W-Fi and Zigbee and thread. Below is chart taken from here showing the latency of Zigbee and thread networks.
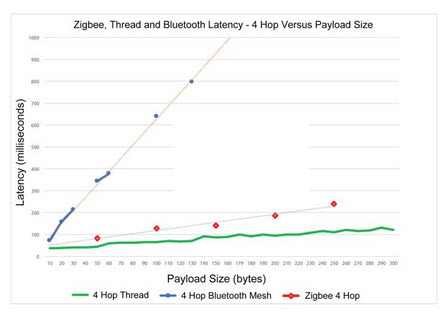
Networking Protocol
The two most popular protocols are TCP and UDP. Because data packets on TCP need acknowledgements it has a higher Latency than UDP. See UDP vs TCP
Network Congestion
The more traffic on a network then the slower that network becomes and the throughput decreases and the latency increases as the network traffic increases.
Intermediate Networking Devices
The more networking devices between sender and receiver then the higher the latency. Software based devices like routers and Gateways have a higher latency than hardware based devices.
End devices and Services
The end device service or application has to process the request and return a response.
The end application maybe for example a web server. How quickly it responds will be determined by the speed of the hardware running it and the load on the server.
Network Latency on Home Networks
The main factor on home networks will be network congestion. This can be caused by file backups, streaming media etc.
In addition the number of devices you have connected will also be an issue.
As mentioned previously Zwave has a higher latency than Zigbee and thread.
As a rule of thumb the larger the network in terms of nodes and the larger the network in terms of distance then the higher the network latency and the more likely it is to be a design issue.
Measuring Network Latency
On TCP/IP networks you can check network latency using the ping and tracert commands. See Windows network commands.
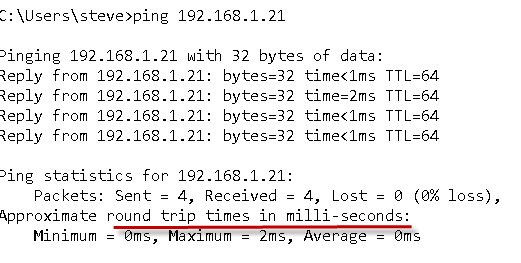
The screen shot below shows the latency using ping measured in milli- seconds.
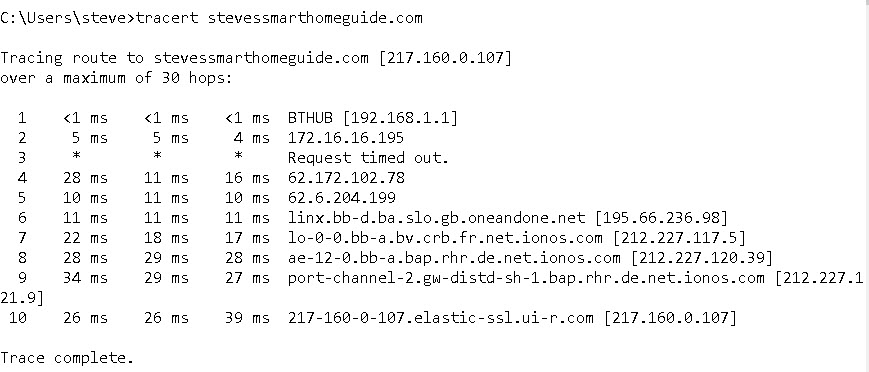
The following is a screen shot using the traceroute command (tracert on windows).
When used on an Internet connection it gives far more detail than a network ping as it will test each segment of the connection.
Common Questions and Answers
Q- Will Doing File Backups during the day Slow down my smart home Network.
A- Probably if you are controlling devices across the Internet.
Q- I have a small Zigbee Network of 10 devices should I worry about Latency.
A- Probably not
Summary
Network Latency is a measure of the delay on a network and is affected by many factors.
Is it something that you need to consider on your own network depends on the number of devices, device types and network size (distance).
Generally a small network (distance and nodes) shouldn’t really have an issue with latency (delay).
Related Tutorials and Resources:
- Video comparing wireless protocols-Matter,Zigbee,Zwave and Wi-Fi
- What is network Latency
- Using Zigbee2MQTT- A Beginners Guide
- Z-Wave Basics – Notes For Beginners