 Privacy considerations aren’t just for those with something to hide.
Privacy considerations aren’t just for those with something to hide.
Most people today use the Internet for shopping, banking and business , and would like to do so privately.
If you use the Internet at home then you are relatively secure from monitoring except by your ISP.
However when using the Internet when travelling is a different matter altogether.
To address these problems there are many companies and organisations offering various privacy solutions based on Proxy servers and VPNs (Virtual Private Networks).
In this tutorial we look at:
- What Your ISP Knows about You
- Who needs a VPN or proxy
- What are VPNs and Proxies
- How do they work and the difference between them.
What Your ISP Knows About You
Most home networks use a router provided by the ISP. The default settings for this router configure all connected clients to use the DNS servers of your ISP.
This means that each time you access a web service the ISP knows about it, and can log it, and even sell on this information to third parties.
Even if you manually edit the DNS settings to use Google or OPenDNS or any other DNS provider then if your ISP uses a technology called transparent DNS proxy they can still intercept your DNS requests and log them.
Who Needs A VPN?
If you:
- Travel and Use Public Wi-Fi Connections.
- Share a Wi-Fi Connection with Others that you don’t know or trust
- Need To surf the web Anonymously.
- Want To access Geographically restricted Content.
- Worried about your Internet Privacy.
then you should take a look at VPNs and Proxy servers.
Proxy Servers- How they Work
Proxy servers are very common in corporate networks where they are used for controlling access to the web.
Because they can control access to websites they are also used by ISPs (Internet Service Providers) like BT to provide services like parental controls.
They are also becoming more popular for normal users who wish to browse the web anonymously.
The way it works is that instead of connecting directly to the website the user connects to the proxy and the proxy connects to the website.
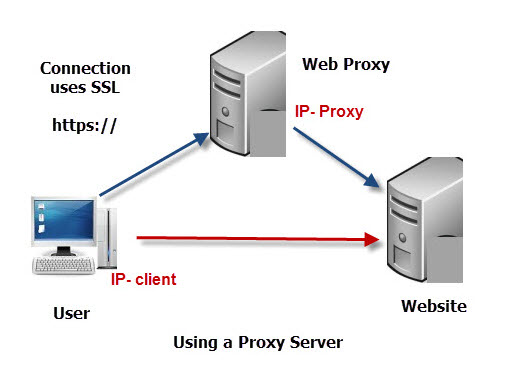 This means that the website sees the IP address of the proxy server, and not the IP address of the user which allows the user to remain anonymous.
This means that the website sees the IP address of the proxy server, and not the IP address of the user which allows the user to remain anonymous.
Proxy servers can, in many circumstances, also allow users access to blocked websites. as the blocking servers are usually on the corporate network or ISP, and they don’t know what sites are being accessed via the proxy.
In addition, if the user’s ISP blocks certain sites by IP address, then they will allow the user access to these sites.
This is because they don’t know that the user is accessing these sites, as they only see the access to the Proxy server.
Problems with Using Proxy Servers
1. Proxy servers work at the application protocol level (see Understanding the OSI Model) )and so can only be used for traffic that uses this protocol. This is normally http.
In plain English this means they generally only work for accessing websites using a web browser.
2. Because all traffic is sent through the proxy you are likely to experience a much slower connection than normal.
3. The Proxy server becomes a security issue as it knows all about you. Can you really trust it? This is especially true when using free Proxy servers.
4. Not all web services will work through a proxy server
5. Not all proxy servers use SSL which means your traffic isn’t encrypted.
VPNs (Virtual Private Networks)- How they Work
VPN or Virtual Private Network is a way of using a public network to carry private data.
A VPN provides a secure and private connection for all traffic from your computer/device, and not just for web browsing traffic.
A VPN works by encrypting the internet connection between your device and the VPN end point.
It provides a secure tunnel for your traffic.
Usually the VPN endpoint is a VPN Gateway located somewhere on the Internet.
The Diagram below depicts a standard internet Connection.
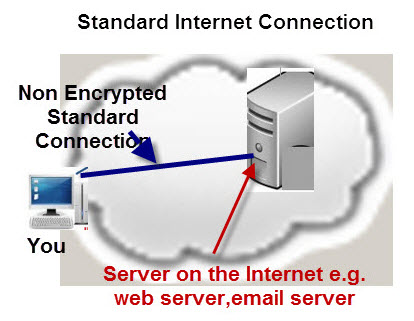
In a standard internet connection the connection can be monitored anywhere along the path from your machine to the the destination server.
The Diagram below shows the same Connection but this time using a VPN Gateway.
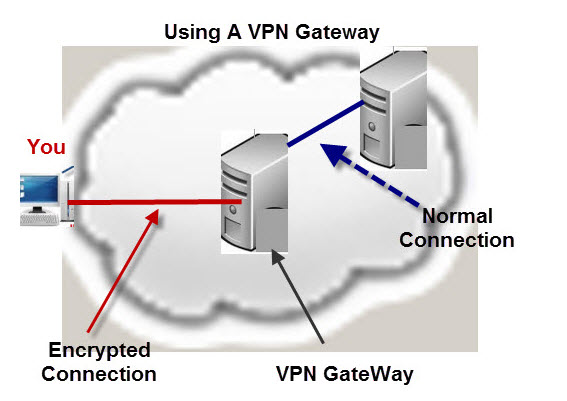 Now the Connection between you and the VPN gateway is secure and only the connection between the gateway and destination server is potentially vulnerable.
Now the Connection between you and the VPN gateway is secure and only the connection between the gateway and destination server is potentially vulnerable.
The connection to the destination server could also be encrypted, if for example, it was a banking server.
A VPN connection supports any application protocol.
So that it could be carrying http or https, ftp or ftps.
The main problem with this is that the VPN gateway is a potential bottleneck, and security risk.
A VPN could also be configured End to End as depicted below:
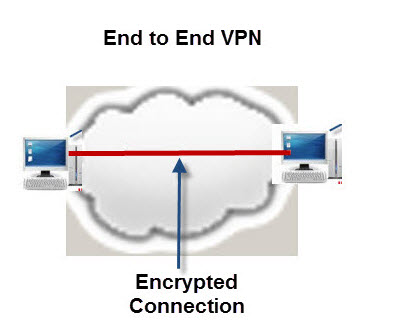
This is common practice for securely linking corporate offices together across the Internet.
SSL (secure sockets layer)
You should note that SSL is the technology that makes your data secure by encrypting it.
SSL connections are used for online shopping, and other services and don’t require you signing up to any service.
The only problem is that you rely on the web server to require it, and currently only servers that need security use it e.g banks and shopping sites.
Google search uses SSL, but this only protects your search data from anyone monitoring your Internet Connection, it doesn’t protect it from Google.
Google still knows who you are, and what you search for and so does your ISP.
However if you do a search via a proxy server or VPN then Google doesn’t know about you unless you happen to be logged into a Google account when you do it.
Proxy vs VPN
A proxy provides for basic anonymous web surfing and doesn’t provide as much security as a VPN.
Proxy services used to be much cheaper than VPN services but this is really no longer the case.
A big advantage of using a proxy is that a proxy doesn’t normally require installing any new software on your device.
However generally I would go for a VPN solution
Client VPN Software
To access a VPN gateway or server from a device e.g. computer or mobile phone you need VPN software installed on that device.
Most VPN providers provide free client software for Windows,Mac an linux as well as Android and IOS.
Most providers have a client limit of around 5 and 6 clients.
VPN Routers
Most home routers allow VPN traffic to pass through but do not them selves offer VPN capability.
However if your router does support this feature then this is an ideal solution for providing VPN for multiple devices as you don’t need to install VPN software on the devices.
It also means that you effectively only use 1 client connection even though you have many devices connected.
If you have smart home devices that don’t support SSL themselves passing their data through a VPN tunnel will help secure them.
This NordVPN video explains it:
If you router doesn’t support this feature and you would like to use it then you would need to change it for one that did or use a two router solution.
VPN Server and Speeds
Because all of your traffic is going through a single server (VPN Gateway) you may find that it is slower than when connecting direct.
The more access servers the VPN provider provides and the proximity of those server to your location then the faster your connection should be.
According to a PC magazine article review a VPN slowed the connection by roughly 60%.
This is not really a problem for normal web browsing, one line banking etc but maybe for streaming video.
VPN Protocols
There are 6 commonly used protocols used for creating a VPN each with their pros and cons, they are:
- PPTP: Fast, widely used and supported
- L2TP/IPSec: Widely used and good speeds
- SSTP: Widely supported and good security
- IKEv2: Fast and mobile-friendly
- OpenVPN: Open source,slow, strongest encryption
- Wireguard: open-source, open-source, growing support
Most providers will support a selection of these protocols.See this makeuseof article
DNS Leaks
You will come across this term when reviewing VPN solutions and it simply means that the DNS traffic is going outside the tunnel and therefore it is insecure.
VPN Kill Switches
Most well known VPN providers provide this feature although it may be called network lock or similar.
The basic idea is that it will block your connection unless it is over the VPN.
This means that if the VPN drops you don’t continue to send data over the network unsecured.
Common Questions and Answers
Q- Should I use a proxy server or a VPN?
A- A proxy server is meant for anonymous browsing, but isn’t necessarily secure. A VPN is secure and always uses SSL to encrypt your data.It works for all applications on your device and not just your web browser.
Q- Can you use SSL connection inside a VPN tunnel?
A-Yes the data just appears like any other date to the VPN
Useful Tutorials and resources
- Home network Security Basics
- What is a VPN
- Proxy servers– Wiki
- Make Your BitTorrent Traffic Anonymous with a Proxy
- DNS leaks and leak test
Very helpful. After your article I went from hopeless to hopeful, finally able to understand better, the VPN how it works, and much much more. Thank you so much.